Required. Absolute or relative path to the Code Inventory JSON report on local disk.
Example: ./ci-reports/avd-prod-ci.json
OpenRewrite is an open source software auto-refactoring tool (OSS project), that can be combined with Code Inventory’s data to automatically deprecate unused and dead code. OpenRewrite can perform semantic analysis and automated refactoring of code using search and transformation recipes. Such recipes are expert, rules-based programs that enable accurate, automated code changes.
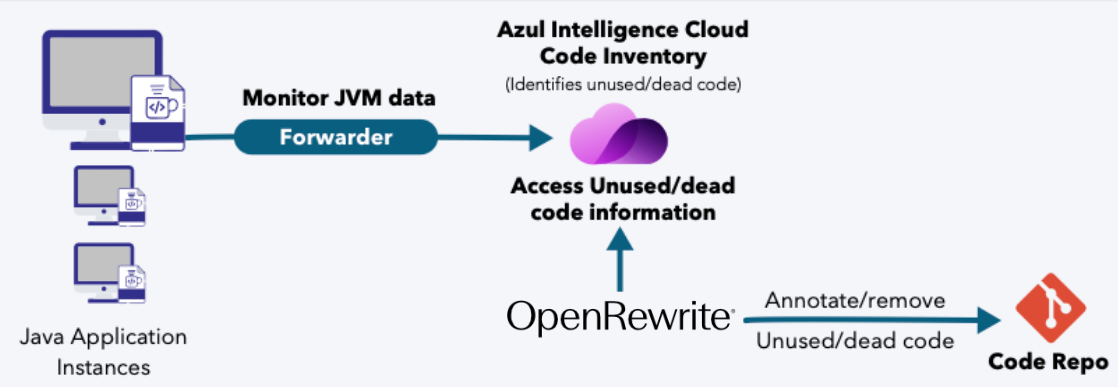
Azul OpenRewrite Plugin is a Maven/Gradle plugin designed to integrate with Azul Code Inventory. Its primary goal is to automatically identify and annotate deprecated code elements within a codebase, based on unused code analysis reports from Azul Intelligence Cloud.
The plugin focuses solely on adding @Deprecated annotations to unused classes. Class removal is left to the customer, as unused classes flagged by Code Inventory may still be referenced elsewhere in the code. Since the resolution of such cases can vary, the plugin avoids making assumptions about how customers prefer to handle them.
The plugin iterates over classes listed in the Code Inventory report that match predefined filters.
The plugin analyzes the report and manages new and existing @Deprecated annotations. If a class has not been used for more than the configured lastSeenAge, an annotation gets added. Also, existing annotations are removed if the class is used again.
All annotations made by your developers will be left untouched.
Generate a Code Inventory report using the Intelligence Cloud Web UI or CLI and save it locally. We recommend to generate a report with the parameters use=ALL, a period of 6 months, and an AppEnvs filter. The report must contain data from the same app as the one is being annotated otherwise the plugin will misbehave.
Create a rewrite.yml file (see Configuring the Plugin) in your project’s root directory and specify which packages and/or classes must be included or excluded. Included ones will be annotated if unused. Excluded ones will be ignored. Take into consideration that excluded has a higher priority than included.
Run the plugin. This will add or remove @Deprecated annotations based on the report. Only the annotation this plugin has added before, will be removed again, no @Deprecated annotations from other sources.
The development team decides which and when deprecated classes get removed from the codebase.
This workflow needs to be repeated to make sure new unused code gets annotated.
|
Note
|
How long Code Inventory monitors your applications, as well as the timing of each phase in the process, is controlled by you. |
The plugin operates on a "Do no harm" policy, and non-existing classes will be ignored.
Imagine you have an application running with different versions. Through an effective use of the AppEnv parameter in your client settings, you can identify those apps with a prefix. For example, the following AppEnv can exist in your environment for the same application in different versions:
my_app_1.24
my_app_1.345_test
my_app_1.1
In this example, use the CONTAINS my_app filter when generating the report to get the data for all these apps. If the naming scheme in your particular case is more complicated, you can use the AppEnvs parameter in the report which supports full regular expressions.
Please note that if data from multiple different applications is combined under the parameters, the results may be inconsistent.
Download the latest version of the plugin from:
The Azul repository:
curl -O https://cdn.azul.com/openrewrite/openrewrite-0.0.13.zip
# OR
curl -O https://cdn.azul.com/openrewrite/openrewrite-latest.zip
Or your Intelligence Cloud Web UI.
Unzip the download.
Install it into your local repository and/or include it in your project, as described below.
You can use the plugin in both Gradle and Maven projects.
In case you are using Gradle, you can use one of the following approaches with a local repository, or by adding the library as part of your project.
Install the downloaded jar-file into your local Maven Repository by running the following command:
mvn install:install-file \
-Dfile=azul-openrewrite-0.0.13.jar \
-DgroupId=com.azul.ic \
-DartifactId=openrewrite-recipe \
-Dversion=0.0.13 \
-Dpackaging=jar \
-DgeneratePom=true
Extend the configuration in your build.gradle file, so it contains:
plugins {
id 'java'
id 'org.openrewrite.rewrite' version '7.18.0'
}
repositories {
mavenLocal()
mavenCentral()
}
dependencies {
rewrite 'com.azul.ic:openrewrite-recipe:0.0.13'
}
rewrite {
activeRecipe(
'Azul', // This name refers to the `name` used in rewrite.yml
)
}
With this configuration, you can run the plugin using this command:
gradle clean build --refresh-dependencies --no-build-cache rewriteRun
Copy the downloaded jar-file into your projects pre-created lib directory.
Extend the configuration in your build.gradle file, so it contains:
plugins {
id 'java'
id 'org.openrewrite.rewrite' version '7.18.0'
}
dependencies {
rewrite files("$rootDir/lib/openrewrite-recipe-0.0.13.jar")
}
repositories {
flatDir dirs: ["$rootDir/lib"]
}
rewrite {
activeRecipe(
'Azul', // This name refers to the `name` used in rewrite.yml
)
}
With this configuration, you can run the plugin using this command:
gradle clean build --refresh-dependencies --no-build-cache rewriteRun
In case you are using Maven, use the following approach:
Create a lib directory into your project and copy the downloaded jar-file into it.
Extend the configuration in your pom.xml file, so it contains:
<project>
...
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.openrewrite.maven</groupId>
<artifactId>rewrite-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>6.22.1</version>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.azul.ic</groupId>
<artifactId>openrewrite-recipe</artifactId>
<version>0.0.13</version>
<scope>system</scope>
<systemPath>${project.basedir}/lib/azul-openrewrite-0.0.13.jar</systemPath>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<configuration>
<activeRecipes>
<recipe>Azul</recipe>
</activeRecipes>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>
With this configuration, you can run the plugin using this command:
mvn clean install -U -Dmaven.build.cache.enabled=false rewrite:run
All plugin behavior is controlled via the rewrite.yml file which you can adjust to your use-case with the following parameters for the com.azul.openrewrite.UnusedClasses recipe in the recipeList.
| Argument | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
ciReport |
string |
Required. Absolute or relative path to the Code Inventory JSON report on local disk. Example: |
appEnvs |
string |
Required. Comma-separated list of AppEnv regular experssions to filter relevant classes that matches that expression from the report. Example: |
classFilter |
string |
Required. Packages to include (filters out third-party code). Example: |
lastSeenAge |
integer |
Required. Threshold in days to consider a class unused. Example: |
exclude |
string |
Classes/packages to ignore. Example: |
logLevel |
enum |
Required. Logging verbosity ( |
maxReportAge |
integer |
Maximum age of the report before the plugin aborts. When you set this to Default value: |
warnReportAge |
integer |
Warn if the report is older than this but still valid. When you set this to Default value: |
type: specs.openrewrite.org/v1beta/recipe
name: Azul
displayName: Mark classes as @Deprecated
description: Processes Code Inventory File to find unused classes
recipeList:
- com.azul.openrewrite.MarkUnusedClasses:
ciReport: "./code_inventory_report.json"
appEnvs: 'NS_Log4jTest_14_Used_darwin24.0,appenv2,e2e_test_\d'
classFilter: org.yourcompany
exclude: com.azul.utils, org.yourcompany.utils
lastSeenAge: 180
logLevel: warn
maxReportAge: 30
warnReportAge: 7