System Components
Table of Contents
Optimizer Hub ships as a Helm chart and a set of Docker images to deploy into a Kubernetes cluster. The Helm chart deploys different components based on the use case.
Architecture Overview
Optimizer Hub offers two deployment options: a full installation of all components or a ReadyNow Orchestrator-only installation.
Full Installation
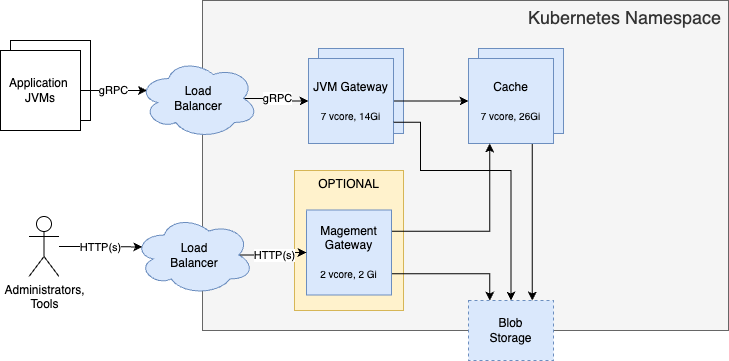
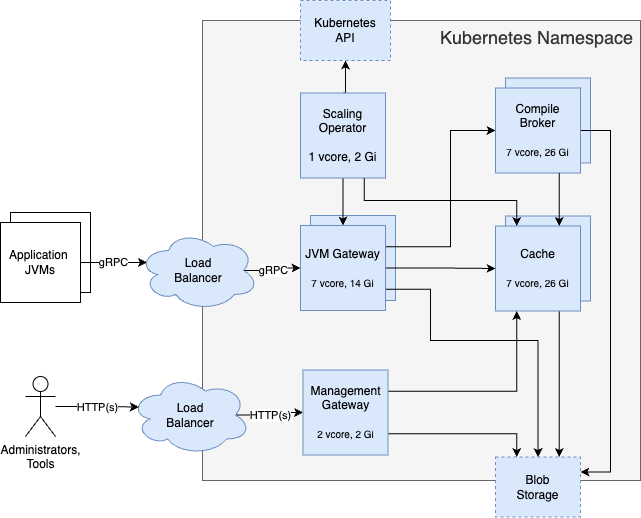
In a full installation, all Optimizer Hub components are available and scale the gateway, compile-broker, and cache when needed.

Remarks:
-
All services use one pod, except Cache uses two pods by default.
-
The load balancer is either your own solution (recommended), or the optional
gw-proxyincluded in Optimizer Hub. See Configuring Optimizer Hub Host for more info.