Installing Optimizer Hub on MicroK8s
MicroK8s can be used for testing, evaluating, and non-cloud-managed blob storage use of Optimizer Hub.
Make sure your MicroK8s meets the 18 vCore minimum for running Optimizer Hub. Although MicroK8s can run on multiple platforms, Optimizer Hub is only available for the x64 platform, so not on macOS with M-processor.
Blob storage is required for Optimizer Hub and can be added to your MicroK8s setup with MinIO.
Installing MicroK8s
Install MicroK8s for your platform following this installation guide.
-
Install MicroK8s on Linux with Snap:
sudo snap install microk8s --classic -
Or, when already installed, start it:
microk8s start -
Check the status while Kubernetes starts:
$ microk8s status --wait-ready microk8s is running high-availability: no datastore master nodes: 127.0.0.1:19001 datastore standby nodes: none -
Turn on these additional services:
# Built-in Kubernetes dashboard microk8s enable dashboard # Metrics used by Optimizer Hub to provide a Grafana dashboard microk8s enable metrics-server -
Access the Kubernetes dashboard:
$ microk8s dashboard-proxy Checking if Dashboard is running. Infer repository core for addon dashboard Waiting for Dashboard to come up. Trying to get token from microk8s-dashboard-token Waiting for secret token (attempt 0) Dashboard will be available at https://127.0.0.1:10443 Use the following token to login: eyJhbGciOiJSUzI1NiIs... -
You can now open the dashboard in the browser, using the token from the previous step.
Installing Optimizer Hub
Optimizer Hub uses Helm as the deployment manifest package manager. There is no need to manually edit any Kubernetes deployment manifests.
-
Make sure your Helm version is
v3.8.0or newer, check it withhelm version. -
Add the Azul Helm repository to your Helm environment:
microk8s helm repo add opthub-helm https://azulsystems.github.io/opthub-helm-charts/ microk8s helm repo update -
Create a namespace (i.e.
my-opthub) for Optimizer Hub.microk8s kubectl create namespace my-opthub -
Clone or download the files from the GitHub opthub-helm-charts repository.
git clone https://github.com/AzulSystems/opthub-helm-charts.git -
Create a directory for your configuration files
mkdir ~/my-opthub/ -
Create MinIO storage:
-
Copy minio-dev.yaml and replace
minio-devwithmy-opthubor the namespace you created in the previous step.cp ~/opthub-helm-charts/minio-dev.yaml ~/my-opthub/minio-dev.yaml sed -i 's/minio-dev/my-opthub/g' ~/my-opthub/minio-dev.yaml # `-i` modifies the original file # `s/old/new/g`: s = substitute, g = all occurrences -
Copy minio-setup-job.yaml and again replace
minio-dev.cp ~/opthub-helm-charts/minio-setup-job.yaml ~/my-opthub/minio-setup-job.yaml sed -i 's/minio-dev/my-opthub/g' ~/my-opthub/minio-setup-job.yaml -
Install the S3 compatible storage with:
microk8s kubectl apply -f ~/my-opthub/minio-dev.yaml -f ~/my-opthub/minio-setup-job.yaml
-
-
Create a configuration file
values-minikube.yaml, based on the example file, to disable all resource definitions.cp ~/opthub-helm-charts/values-minikube.yaml ~/my-opthub/values-minikube.yamlModify the following value to match your environment:
# Existing storageEndpoint: http://minio.minio-dev.svc.cluster.local:9000 # Change to storageEndpoint: http://minio.my-opthub:9000 -
Create the configuration files for the monitoring tools (Prometheus and Grafana).
-
A file is needed for the role creation:
metrics-rbac.yaml-
Copy the file from the GitHub opthub-helm-charts repository.
-
Replace the namespace in two places
namespace: opthubin the example file, or execute:sed -i 's/opthub$/my-opthub/g' ~/my-opthub/metrics-rbac.yaml -
If you create your service accounts separately, you need to match these names with the ones in this file.
-
Apply these roles to your minikube:
microk8s kubectl apply -f ~/my-opthub/metrics-rbac.yaml
-
-
Create a file with the monitoring configuration:
values-monitoring.yaml-
Copy the file from the GitHub opthub-helm-charts repository.
-
If you created your own service account, update this value in the file:
name: metrics-server.
-
-
Install the Kubernetes State Metrics service:
microk8s helm install kube-state-metrics \ oci://ghcr.io/prometheus-community/charts/kube-state-metrics
-
-
Install using Helm, passing in the
values-minikube.yaml. In case you don’t want to install the full Optimizer Hub, but only a part of the services, first check "Configuring the Active Optimizer Hub Services".microk8s helm install opthub opthub-helm/azul-opthub \ -n my-opthub \ -f ~/my-opthub/values-minikube.yaml \ -f ~/my-opthub/values-monitoring.yamlThe command should produce output similar to this:
NAME: opthub LAST DEPLOYED: Tue Jun 17 16:52:18 2025 NAMESPACE: my-opthub STATUS: deployed REVISION: 1 TEST SUITE: None -
Verify that all started pods are ready:
$ microk8s kubectl get all -n my-opthub NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE pod/cache-0 0/1 Running 0 26s pod/compile-broker-68d58bbc8d-nqj2z 0/1 Running 0 26s pod/gateway-68d84f7fff-zwpx4 0/1 Running 0 26s pod/grafana-56c957b967-4r9w2 0/2 ContainerCreating 0 26s pod/gw-proxy-5bf785bdbc-fl586 1/1 Running 0 26s pod/mgmt-gateway-5c556bd89f-rxd24 0/1 Running 0 26s pod/minio 1/1 Running 0 4m23s pod/minio-setup-job-t29vv 0/1 Completed 1 4m23s NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE service/cache ClusterIP None <none> 5701/TCP 26s service/compile-broker ClusterIP 10.152.183.211 <none> 50051/TCP 26s service/gateway LoadBalancer 10.152.183.161 <pending> 50051:30759/TCP 26s service/gateway-headless ClusterIP None <none> 50051/TCP 26s service/grafana NodePort 10.152.183.49 <none> 80:32146/TCP 26s service/grafana-headless ClusterIP None <none> 9094/TCP 26s service/mgmt-gateway LoadBalancer 10.152.183.185 <pending> 8080:32188/TCP 26s service/minio ClusterIP 10.152.183.106 <none> 9000/TCP,9090/TCP 4m23s service/prometheus-server ClusterIP 10.152.183.235 <none> 80/TCP 26s NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE deployment.apps/compile-broker 0/1 1 0 26s deployment.apps/gateway 0/1 1 0 26s deployment.apps/grafana 0/1 1 0 26s deployment.apps/gw-proxy 1/1 1 1 26s deployment.apps/mgmt-gateway 0/1 1 0 26s deployment.apps/prometheus-server 0/1 0 0 26s NAME DESIRED CURRENT READY AGE replicaset.apps/compile-broker-68d58bbc8d 1 1 0 26s replicaset.apps/gateway-68d84f7fff 1 1 0 26s replicaset.apps/grafana-56c957b967 1 1 0 26s replicaset.apps/gw-proxy-5bf785bdbc 1 1 1 26s replicaset.apps/mgmt-gateway-5c556bd89f 1 1 0 26s replicaset.apps/prometheus-server-59588969fc 1 0 0 26s NAME READY AGE statefulset.apps/cache 0/1 26s NAME STATUS COMPLETIONS DURATION AGE job.batch/minio-setup-job Complete 1/1 11s 4m23s -
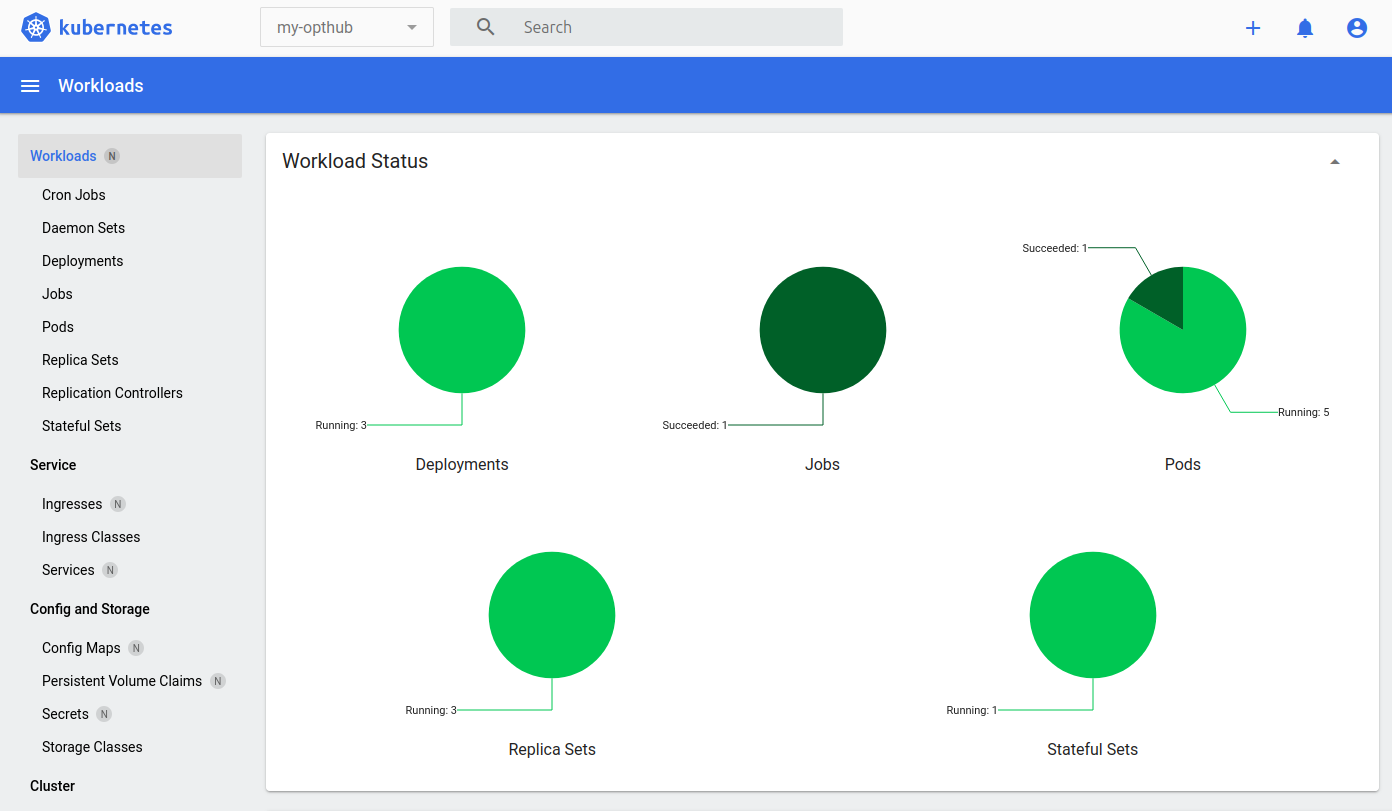
You can also verify the status on the dashboard we opened before, by selecting the
my-opthubnamespace in the header:
-
Add port forwarding to have access to Grafana:
microk8s kubectl port-forward -n my-opthub deployments/gw-proxy 3000:3000 -
The Grafana dashboard is now available on
localhost:3000. At this moment, it only shows minimal data. Use this dashboard later, when you have connected your first clients.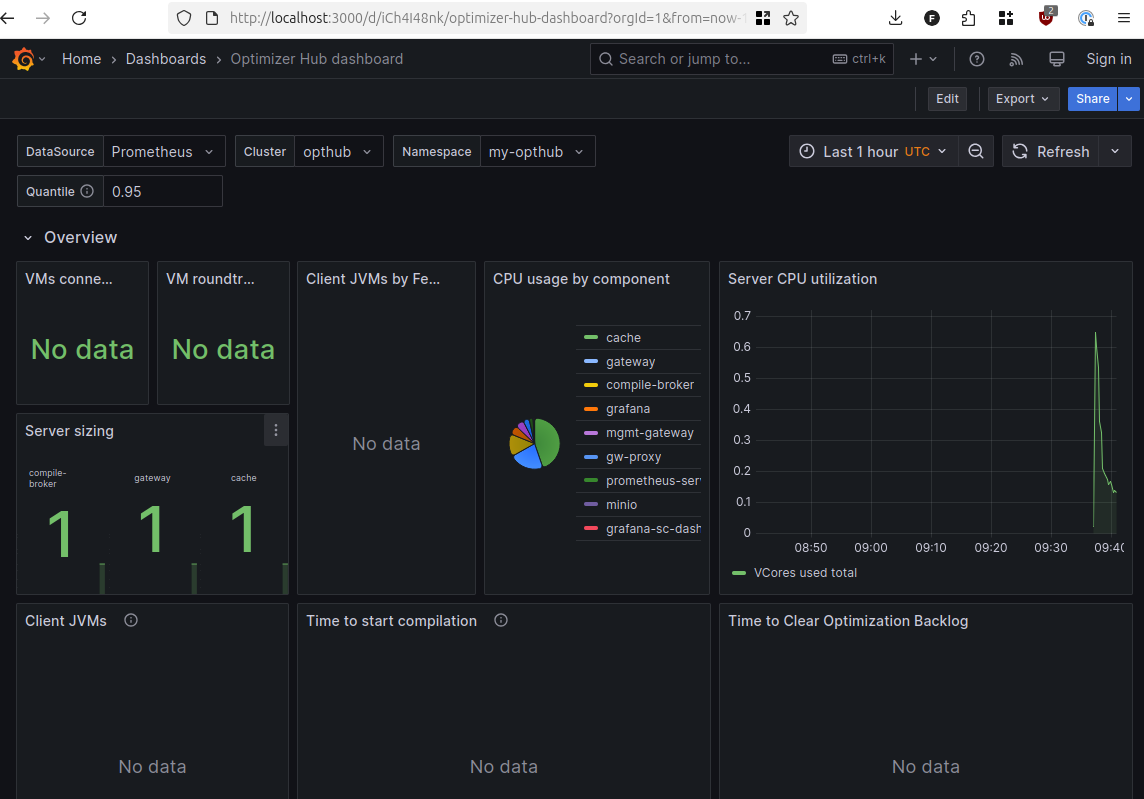
Upgrade Optimizer Hub on MicroK8s
You can upgrade your Optimizer Hub instance running on MicroK8s, and keep all profile data and compile caches as the S3 compatible minio storage won’t be upgraded.
-
List the currently installed version:
$ microk8s helm list --namespace my-opthub NAME NAMESPACE REVISION UPDATED STATUS CHART APP VERSION opthub my-opthub 1 2025-06-17 16:59:26.33115804 +0200 CEST deployed azul-opthub-1.11.2 1.11.2 -
List the available versions on the helm repo:
$ microk8s helm repo update $ microk8s helm search repo opthub-helm --versions NAME CHART VERSION APP VERSION DESCRIPTION opthub-helm/azul-opthub 1.11.2 1.11.2 Azul Intelligence Cloud: Optimizer Hub opthub-helm/azul-opthub 1.11.1 1.11.1 Azul Intelligence Cloud: Optimizer Hub opthub-helm/azul-opthub 1.11.0 1.11.0 Azul Intelligence Cloud: Optimizer Hub opthub-helm/azul-opthub 1.10.2 1.10.2 Azul Intelligence Cloud: Optimizer Hub opthub-helm/azul-opthub 1.10.1 1.10.1 Azul Intelligence Cloud: Optimizer Hub opthub-helm/azul-opthub 1.10.0 1.10.0 Azul Intelligence Cloud: Optimizer Hub opthub-helm/azul-opthub 1.9.5 1.9.5 Azul Intelligence Cloud: Optimizer Hub ... -
Upgrade and use the same settings and files from the installation, just by replacing
installwithupgrade:microk8s helm upgrade opthub opthub-helm/azul-opthub -n my-opthub -f ~/my-opthub/values-minikube.yamlNoteTo upgrade or downgrade to a specific version, add --version <version>. -
After upgrading, verify the version with the helm list command again.
-
You can check the version of the MinIO storage with this command:
$ microk8s kubectl exec -n my-opthub pod/minio -- minio --version minio version RELEASE.2024-12-18T13-15-44Z (commit-id=16f8cf1c52f0a77eeb8f7565aaf7f7df12454583)
Uninstalling Optimizer Hub from MicroK8s
Optimizer Hub can be removed from minikube using helm, after which the namespace can also be deleted.
microk8s helm uninstall opthub -n my-opthub
microk8s kubectl delete namespace my-opthub
microk8s kubectl delete -f testing-rbac.yaml
microk8s helm repo remove opthub-helm